The Role of Space Telescopes in Modern Astronomy
The Role of Space Telescopes in Modern Astronomy stand as humanity’s inventive miracles, investigating the profundities of the universe from their vantage centers past Earth’s current circumstances. These remarkable instruments have reshaped how we can decipher the universe, revealing heavenly wonders across a great many frequencies and opening critical insider facts that reach from the acquaintance of stars with faint matter and energy. This comprehensive examination plunges into the basic responsibilities, mechanical movements, key missions, sensible disclosures, prospects, and hardships introduced by space telescopes in the field of current cosmology.
TOPIC : the-challenges-of-interstellar-travel
Preamble to Space Telescopes
Space telescopes address the pinnacle of observational stargazing, offering unequaled abilities to focus on the universe with clearness and precision. Put in a circle over the distorting effects of Earth’s air, these instruments get light across the electromagnetic reach, from radio waves to gamma radiates. Consequently, they give analysts quick and dirty pieces of information about the piece, components, and improvement of heavenly things and eccentricities.
Mechanical Movements

Optical and Infrared Telescopes
Among the most striking space telescopes is the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), shipped off in 1990 by NASA and functioned collectively with the European Space Association (ESA). Hubble has become indivisible from shocking pictures of distant universes, nebulae, and brilliant gatherings, offering cosmologists uncommon points of view on galactic idiosyncrasies in clear and splendid frequencies. Its discernments have not quite recently disturbed how we could decipher vast turn of events and the possibility of dim openings yet furthermore expected a critical part in concluding the expansion speed of the universe.
Hubble Space Telescope (HST)
The Hubble Space Telescope has outperformed all presumptions since it was sent into the low Earth circle. Outfitted with a 2.4-meter fundamental mirror and different consistent instruments, Hubble has gotten positive pictures that have shaped our point of view on the universe. Its insights have gone from researching the components of planetary environments inside our planetary gathering to assessing the earliest frameworks outlined after the Immense blast. Hubble’s responsibilities to stargaze length a wide show of focuses, from the revelation of new moons around Pluto to the preparation of dull matter courses in grandiose framework gatherings.
James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)
Reserved for a farewell in 2024, the James Webb Space Telescope tends to the accompanying backwoods in space-based stargazing. Named after NASA’s resulting executive, JWST is expected to succeed Hubble as the main observatory for focusing on the universe. It will work essentially in the infrared reach, offering noteworthy responsiveness and objective for seeing far away universes, star-outlining regions, and exoplanetary structures. JWST’s undeniable level instruments, including its partitioned fundamental mirror and set-up of consistent locators, commitment to changing how we can decipher the early universe and give essential encounters into the turn of events and progression of planetary systems.
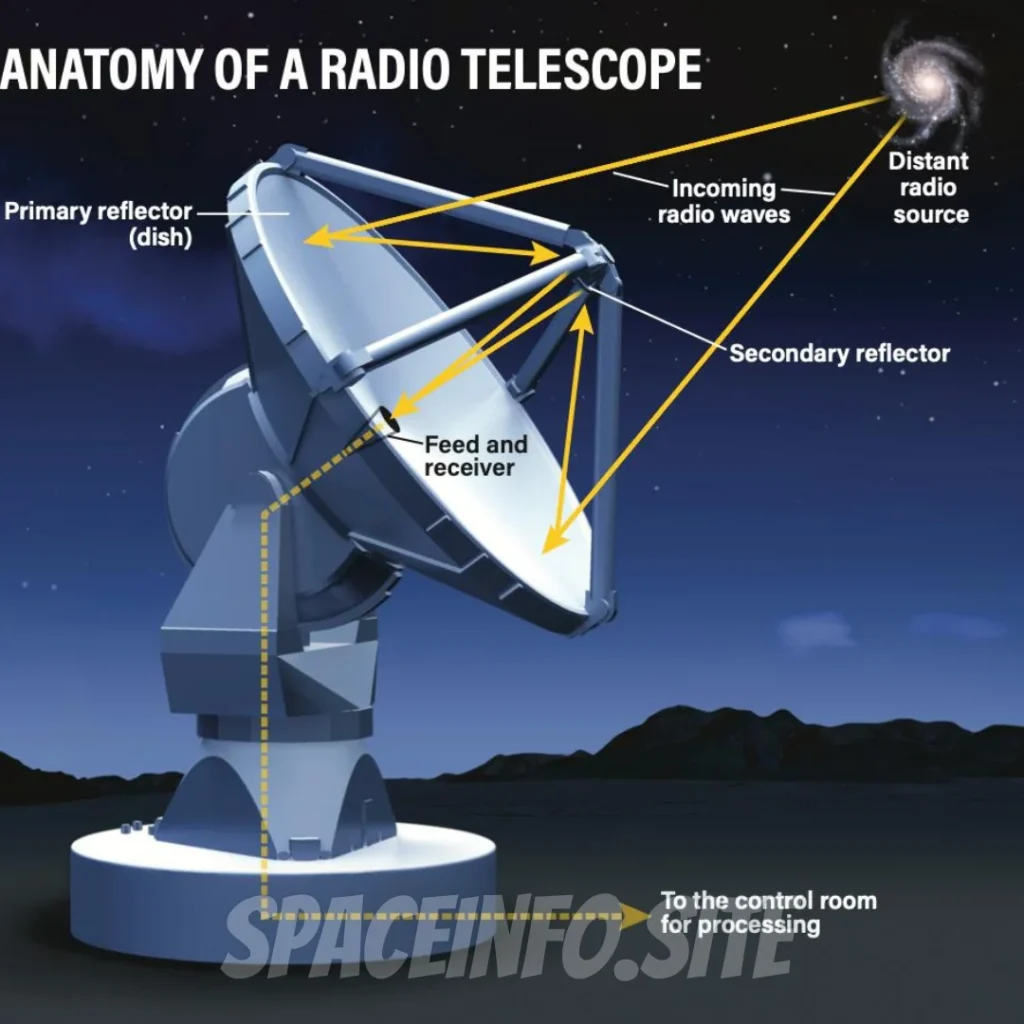
Radio Telescopes
Despite optical and infrared telescopes, space-based observatories consolidate radio telescopes that perceive and take apart radio waves emanated by divine articles. Models consolidate the Very Immense Group (VLA) in New Mexico and the Atacama Tremendous Millimeter/submillimeter Show (ALMA) in Chile. These instruments work in focusing on vainglorious microwave establishment radiation, arranging sub-nuclear fogs, and seeing pulsars and quasars. Radio telescopes give equal data to optical discernments, revealing hidden away plans inside frameworks and testing the beginning stages of cosmic fascination.
X-shaft and Gamma-pillar Telescopes
At the high-energy finish of the electromagnetic reach, space telescopes notice X-pillars and gamma radiates communicated by sources like dull openings, inestimable blast remnants, and dynamic infinite centers. The Chandra X-shaft Observatory and the Fermi Gamma-bar Space Telescope are two prominent examples of telescopes focused on these frequencies. They focus on the savage cycles happening near supermassive dim openings, map the movement of huge shafts across the Smooth Way enormous framework, and inspect faint matter through indirect distinguishing proof methods. X-shaft and gamma-bar telescopes give fundamental pieces of information into the most energetic events known to man, including the effects of framework bundles and the advancement of gamma-pillar detonates.
Key Space Telescope Missions
Kepler Space Telescope
Shipped off in 2009, the Kepler Space Telescope transformed how we could decipher planetary systems past our planetary gathering. Kepler’s fundamental mission was to search for exoplanets by noticing the quality of stars for periodic dives achieved through planetary ventures. Over its utilitarian lifetime, Kepler viewed a large number of insisted and promising new kid in-town exoplanets, recollecting harsh universes for the reasonable zones of their parent stars. These disclosures have given dire data to understanding planetary course of action processes and evaluating the inescapability of Earth-like planets in our astronomical framework.
Spitzer Space Telescope
Utilitarian from 2003 to 2020, the Spitzer Space Telescope was NASA’s infrared observatory, investing critical energy focusing on the universe at frequencies going from 3 to 180 micrometers. Spitzer’s insights gave encounters into the star course of action inside thick sub-nuclear fogs, the advancement of planetary systems, and the blend of interstellar buildup grains. Its legacy consolidates arranging the infrared transmission from universes across galactic time, uncovering the characteristics of supermassive dim openings in astronomical centers, and distinguishing the warm radiation from contiguous exoplanets. Spitzer’s disclosures continue to affect current and future missions in infrared cosmology, including the James Webb Space Telescope.
Intelligent Revelations Enabled by Space Telescopes

Exoplanet Examination
One of the principal responsibilities of Room telescopes has been the revelation and depiction of exoplanets orbiting stars past our close-by planet bunch. The journey for exoplanets began unequivocally with ground-based observatories at this point got a move on with the farewell of given space missions like Kepler and the Voyaging Exoplanet Study Satellite (TESS). These telescopes use the movement strategy to recognize exoplanets passing before their parent stars, causing a short-lived decreasing in wonder conspicuous from Earth. By assessing the timing and length of these movements, stargazers can prompt the size, orbital period, and now and again the association of faraway universes.
Cosmological Encounters
Space telescopes play had a critical effect in trimming how we could decipher the universe’s plan, improvement, and outrageous predetermination. Impression of distant supernovae, self-important microwave establishment radiation, and the enormous degree dispersal of universes have given key data concentration to cosmological models, including the Lambda Cold Faint Matter (ΛCDM) model. This construction depicts a universe overpowered by dull energy, a confounding power driving the accelerated improvement of Room, and faint matter, a subtle substance that teams up gravitationally with standard matter and radiation.
By focusing on the tremendous microwave establishment with instruments, for instance, the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Test (WMAP) and the Planck transport, space specialists have arranged the temperature instabilities left over from the Enormous blast, revealing the seeds of future world turn of events and insisting the age of the universe to inside 1% accuracy.
Dull Opening Assessments
Among the most puzzling areas of strength for and known to man are dull openings, regions of spacetime where gravity is outrageous so much that not even light can escape. Space telescopes play had a critical effect in seeing and depicting dull openings across the electromagnetic reach, from radio waves to gamma radiates. Supermassive dull openings stay at the focal point of most universes, including our Smooth Way, and expect a fundamental part in coordinating star improvement and framework advancement.
By following the circles of stars and gas fogs near these galactic behemoths, space specialists can measure their masses and understand the presence of event horizons, the breaking point past which nothing can escape. Dim openings similarly release solid planes of radiation and particles that should be visible to radio and X-shaft telescopes, giving encounters into the patterns of collection and relativistic plasma material science.
Future Possibilities and Difficulties
Cutting edge Telescopes
The fate of Space-based space science is brilliant, with a few cutting-edge telescopes ready to proceed with the tradition of Hubble, Spitzer, and Kepler. The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) addresses a quantum jump in infrared responsiveness and goal, empowering stargazers to concentrate on the earliest worlds and the climates of possibly livable exoplanets. Booked for send-off on an Ariane 5 rocket from French Guiana, JWST is a joint undertaking of NASA, the European Space Organization (ESA), and the Canadian Space Organization (CSA) that will work from a circle around the second Lagrange point (L2) of the Earth-Sun framework. JWST’s 6.5-meter essential mirror is made out of 18 hexagonal fragments covered with an infinitesimally flimsy layer of gold, permitting it to catch faint infrared light from the far-off scopes of the universe. Its four science instruments incorporate the Close to Infrared Camera (NIRCam), the Close to Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec), the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), and the Fine Direction Sensor/Close to Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (FGS/NIRISS), each intended to work at explicit frequencies and goals. Notwithstanding JWST, other future space telescopes incorporate the Nancy Effortlessness Roman Space Telescope (previously WFIRST) and the Trendsetting innovation Huge Opening Space Telescope (ATLAST), the two of which vow to extend the wildernesses of astrophysical exploration.
Innovative and Monetary Difficulties
Regardless of their logical potential, space telescopes face various difficulties concerning innovative turn of events, subsidizing, and functional coordinated factors. The development of enormous scope observatories, for example, JWST requires exact designing and getting together of touchy parts in clean-Space conditions. Furthermore, the sending and support of Space telescopes in a low Earth circle (LEO) or geostationary circle (GEO) presents strategic difficulties for mission organizers and shuttle engineers. One more thought is the financing expected to help long-haul logical exploration projects, which can cost billions of dollars worth of quite a few years. These difficulties are intensified by political and financial variables that impact the assignment of assets among contending needs inside public space
organizations and global consortia. Thus, space telescopes frequently depend on cooperation between legislatures, scholastic foundations, and confidential area accomplices to subsidize and coordinate exploration endeavors.
End
All in all, space telescopes have upset how we might interpret the universe by giving uncommon perspectives on heavenly items and peculiarities across the electromagnetic range. From the notable pictures caught by Hubble to the impending disclosures guaranteed by JWST and future missions, these instruments keep on moving marvel and interest in the universe’s boundlessness and intricacy. As stargazers and designers push the limits of observational cosmology, space telescopes will assume a crucial part in responding to basic inquiries concerning the idea of dull matter and energy, the starting points of planetary frameworks, and the potential for life past Earth. By embracing mechanical advancement and global cooperation, mankind can keep on investigating the universe’s secrets and extend our aggregate information on the universe.